
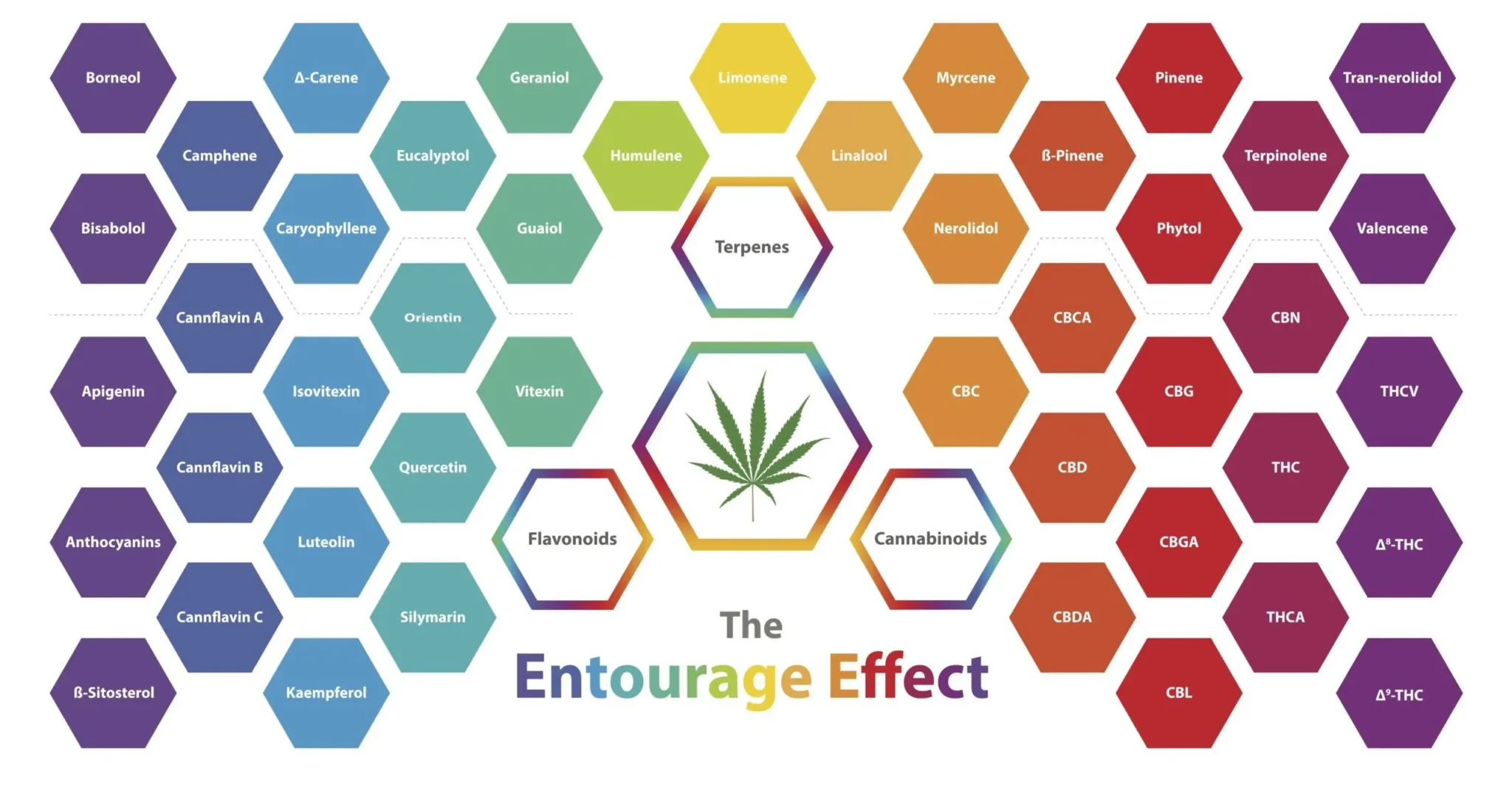
Cannabis is known to contain over 500 different secondary metabolites, and this number continues to grow as research on the plant advances. The primary classes of secondary metabolites found in cannabis are cannabinoids, terpenes, and flavonoids.
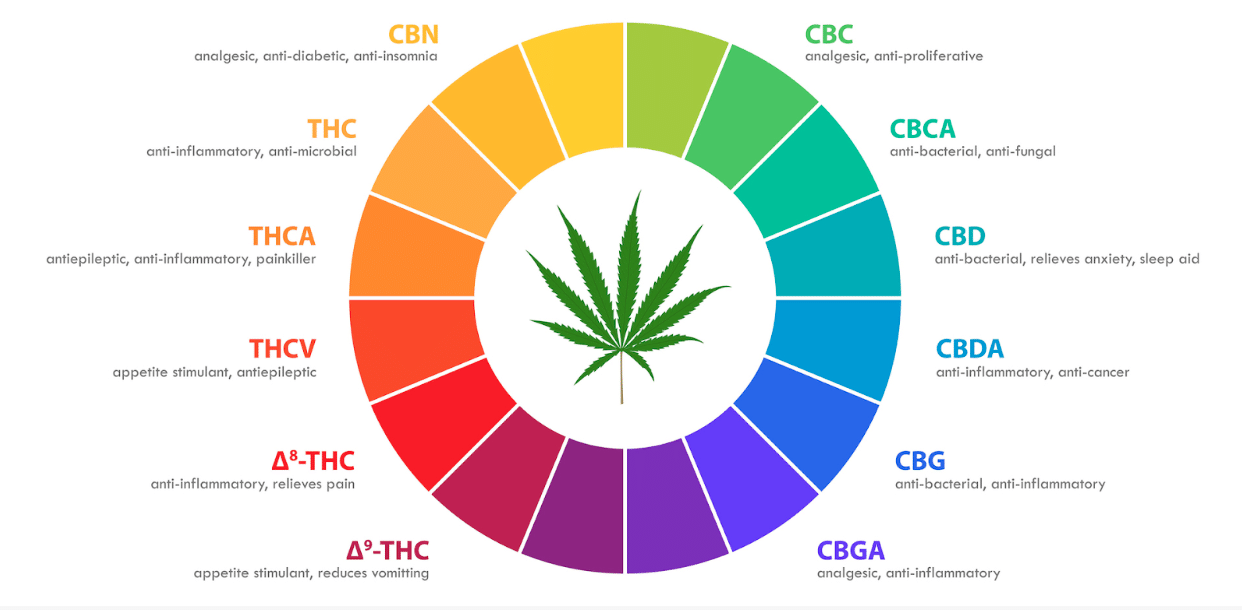
Clayborn https://www.claybourneco.com/blog/what-are-cannabinoids-definition-effects-and-benefits
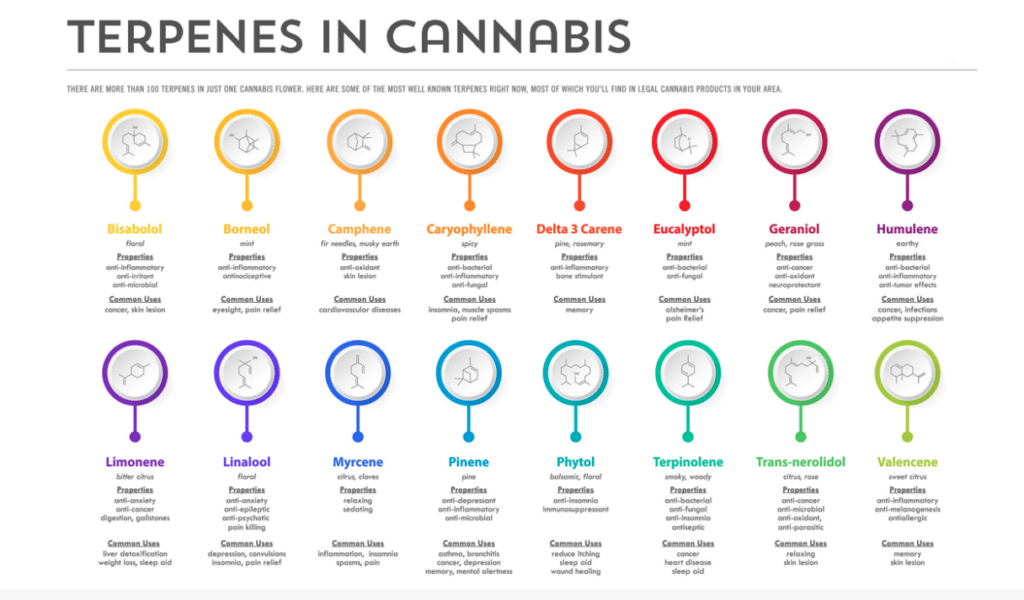
https://thekindgoods.com/terpenes-what-they-are-and-why-do-they-help/
Cite: https://elevate-holistics.com/blog/cannabis-flavonoids-what-are-those/
Cannabinoids, Terpenes, and Flavonoids
Cannabinoids:
These are the most well-known secondary metabolites in cannabis. There are more than 100 known cannabinoids in the plant, with the most famous being THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) and CBD (cannabidiol).
Terpenes:
The Study in Focus: Researchers examined commercial cannabis samples, all cloned from a common parent but cultivated in contrasting environments. Outdoor Terpenes are aromatic compounds found in various plants, including cannabis. They contribute to the plant’s distinct aroma and flavor. Cannabis contains a wide range of terpenes, such as myrcene, limonene, pinene, and linalool. Terpenes also have potential therapeutic effects and can modulate the effects of cannabinoids through the entourage effect.
Flavonoids:
While less well-studied compared to cannabinoids and terpenes, flavonoids in cannabis have shown antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Some common flavonoids in cannabis include quercetin, kaempferol, and apigenin.
These secondary metabolites play various roles in the cannabis plant’s biology and contribute to the plant’s overall pharmacological profile, affecting the taste, smell, and therapeutic properties of cannabis products.
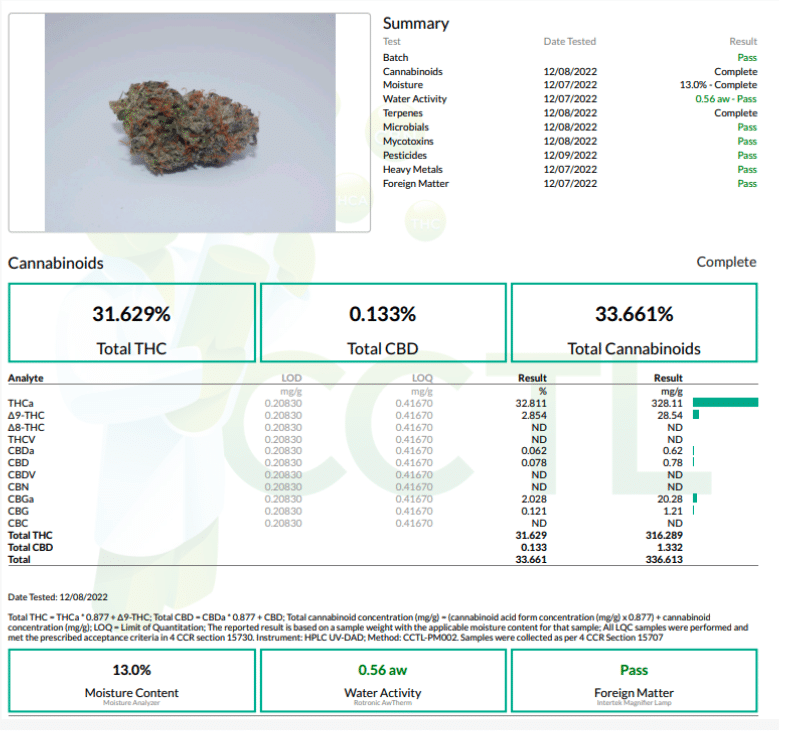
It’s important to remember that the more Terpenes and Cannabinoids you test for the higher your test results will be. Are you testing for 100 cannabinoids and 100 terpenes?
Processes and Methods:
Cannabis testing laboratories use various processes and methods to assess the potency of cannabis. The specific tests conducted may vary by region, regulations, and the services offered by the lab but commonly performed tests in cannabis testing labs include:
Potency Testing: This involves measuring the levels of cannabinoids in the cannabis product, including THC (tetrahydrocannabinol), CBD (cannabidiol), and others. High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and gas chromatography (GC) are common techniques for potency testing.
Pesticide Residue Testing: Cannabis plants are susceptible to pests and may be treated with pesticides during cultivation. Pesticide residue testing checks for the presence of harmful pesticide residues to ensure product safety. Liquid or gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS or GC-MS) may be used for this purpose.
Terpene Profiling: Terpenes are aromatic compounds in cannabis that contribute to its flavor and aroma. Terpene profiling involves identifying and quantifying these compounds, often using GC or HPLC.
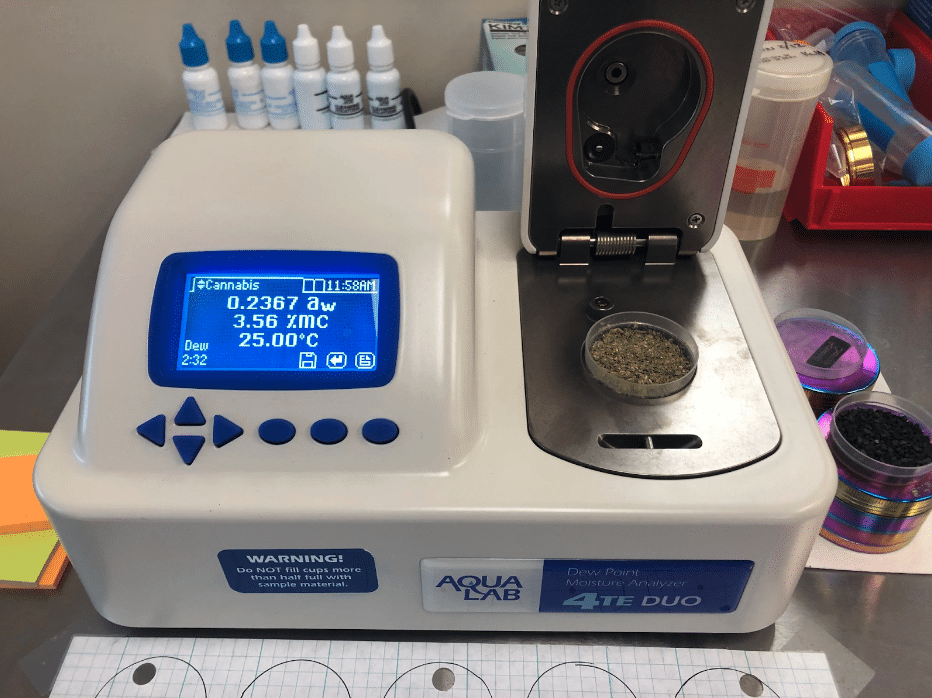
Moisture Content Analysis: This determines the moisture content in cannabis flowers and products, as it can affect product quality and consistency. It’s usually measured using a moisture balance or oven drying method.
Cannabinoid and Terpene Stability Testing: This assesses how cannabinoids and terpenes change over time, helping to determine product shelf-life and stability.
Cannabis testing laboratories typically follow good laboratory practices (GLP) and adhere to strict quality control and quality assurance protocols to ensure the accuracy and reliability of their results but mistakes do happen.
Two different cannabis testing facilities, two different test results:
There can be several reasons why two different cannabis testing facilities might produce different test results for the same batch of cannabis. These variations can be attributed to factors related to the testing process, sample preparation, equipment, and the inherent variability of the cannabis plant.
Team Elite Genetics
Here are some common reasons for discrepancies in test results:
Methodology Differences: Different testing facilities may use different testing methodologies or instruments. These variations in testing methods can lead to differences in results, especially if one method is more sensitive or precise than another.
Sample Preparation: The way the cannabis sample is prepared for testing can impact the results. Variations in how samples are homogenized, ground, or extracted can lead to differences in cannabinoid and contaminant levels.
Equipment Calibration: Testing equipment must be regularly calibrated and maintained to ensure accuracy. If one facility’s equipment is not properly calibrated or maintained, it can produce inaccurate results.
Human Error: Human error can occur at any stage of the testing process, from sample collection to data entry. Mistakes in labeling, data recording, or sample handling can lead to discrepancies in results.
Variability in the Plant Material: Cannabis plants can have natural variability in cannabinoid and terpene profiles, even within the same batch. Differences in the portion of the plant tested (buds, leaves, stems) can also contribute to variations in results.
Sample Heterogeneity: Cannabis flowers are not uniform in terms of cannabinoid distribution. If the samples taken for testing are not representative of the entire batch, it can lead to differences in results.
Contamination: Contaminants present in the testing facility, such as cross-contamination between samples or issues with laboratory cleanliness, can affect results.
Test Sensitivity: The sensitivity of the testing methods used can also play a role. Some facilities may use more sensitive equipment or methods that can detect lower levels of cannabinoids or contaminants.
Variability in State Regulations: Different regions and states may have varying regulations and testing requirements for cannabis, leading to differences in testing practices and results.
To minimize these discrepancies and ensure accuracy, it’s important for the cannabis industry to establish and adhere to standardized testing protocols, quality control measures, and accreditation processes. Regular proficiency testing and inter-laboratory comparisons can also help ensure the reliability of cannabis testing results. Consumers and businesses should work with reputable testing facilities that follow best practices and adhere to relevant regulations.
Water content:
Important to note, that the water content of cannabis can significantly impact test results for its potency.
https://www.labmanager.com/big-picture/ensuring-quality-in-cannabis-and-hemp-testing/keys-to-successfully-certifying-your-cannabis-or-hemp-testing-lab-27132
Issues related to water content:
Dilution Effect: Cannabis plants with higher moisture content will have a lower concentration of cannabinoids by weight because the cannabinoids are diluted by the water. This means that if a sample of cannabis with a high moisture content is tested for potency, it may appear to have a lower potency than it actually does once the moisture is removed.
Inaccurate Potency Estimates: Testing labs typically report cannabinoid content as a percentage of the dry weight of the sample. If the moisture content is not properly accounted for, the reported potency can be misleading. This is why many testing labs use a process called “moisture content analysis” to determine the water content of a cannabis sample before performing potency testing.
Variability: Cannabis moisture content can vary widely depending on factors like cultivation methods, environmental conditions, and post-harvest handling. This variability can make it challenging to obtain consistent and accurate potency test results without proper moisture content analysis.
Aqualab 4- moisture content and water activity. https://medicinecreekanalytics.com/water-activity-testing/
In conclusion:
The intricate world of cannabis secondary metabolites, including cannabinoids, terpenes, and flavonoids, contributes to the plant’s diverse properties. Understanding the factors influencing testing outcomes, such as methodology, sample handling, and equipment calibration, is vital for accurate results. Moisture content plays a crucial role in potency assessments, emphasizing the need for comprehensive analysis. To ensure reliability, standardized protocols, rigorous quality control, and accreditation are paramount. By embracing these practices, the cannabis industry can navigate the complexities of testing, empowering cultivators, businesses, and consumers with informed decision-making and allocation of resources.















Leave A Comment