
The cannabis industry has witnessed remarkable growth over the past few years, driven by the evolving legal landscape and increased demand for its products. However, maintaining optimal environmental conditions within cannabis cultivation facilities is crucial for ensuring high-quality yields and minimizing risks. This article explores various aspects of measuring and controlling heat in cannabis cultivation facilities, including the use of infrared technology, remote ballasts for lighting, impact assessment on leaf temperature, and the significance of efficient airflow. Furthermore, it presents a formula for calculating the sensible load in these spaces. By implementing these strategies, cannabis cultivators can better manage their operations and maximize productivity.
Intro:
Cannabis cultivation requires a delicate balance of environmental factors to ensure healthy plant growth and maximize yield. Temperature control is one of the most critical aspects of this process, as deviations can lead to undesirable outcomes such as reduced yield, compromised product quality, and increased risks of diseases and pests. This article delves into various techniques and methods for measuring and controlling heat in cannabis cultivation facilities to maintain an optimal environment conducive to plant growth.
-
Using Infrared Technology to Measure Heat:
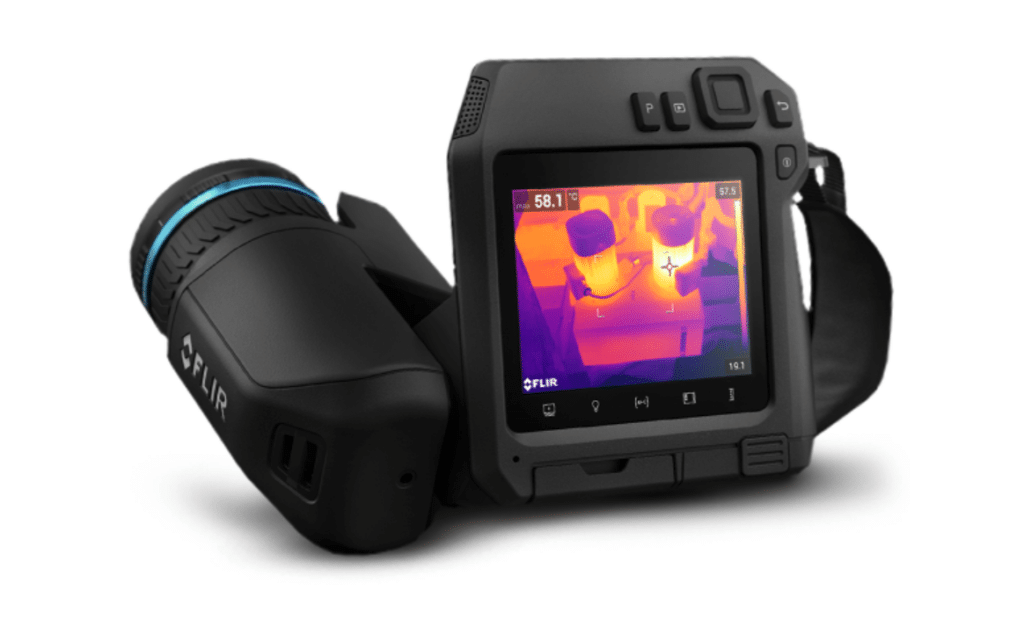
Infrared (IR) technology has gained popularity in the cannabis industry for its non-invasive and accurate heat measurement capabilities. Infrared thermography allows cultivators to visualize temperature variations across the cultivation space, providing valuable insights into heat distribution. These images can help identify hotspots or areas where temperature control is needed.
Flir Heat Guns
-
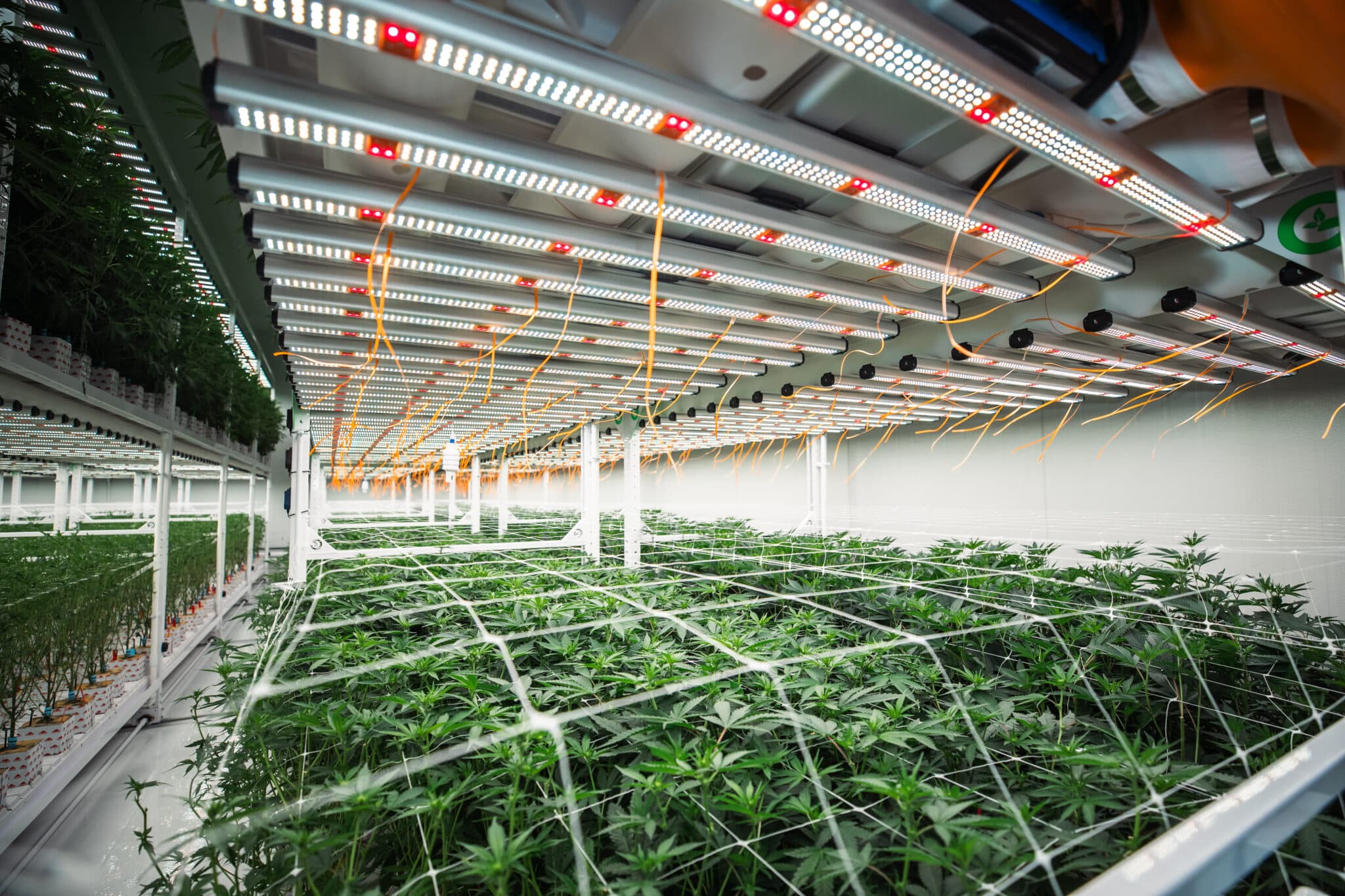
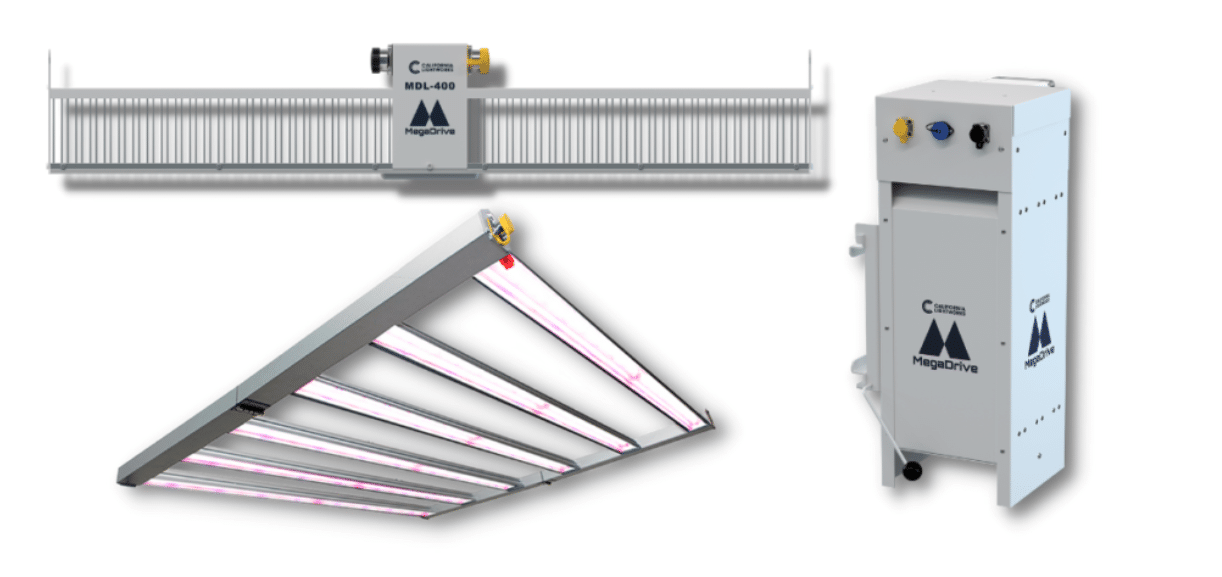
Utilizing Remote Drivers for Lighting:
Lighting is essential for cannabis cultivation, but it often generates heat that can disrupt the optimal temperature conditions within the facility. Remote drivers are a solution to this problem, as they separate the lighting components from the grow room. This not only reduces heat emissions but also minimizes the risk of electrical fires, creating a safer and more controlled environment.
Remote drivers: California Lightworks
-
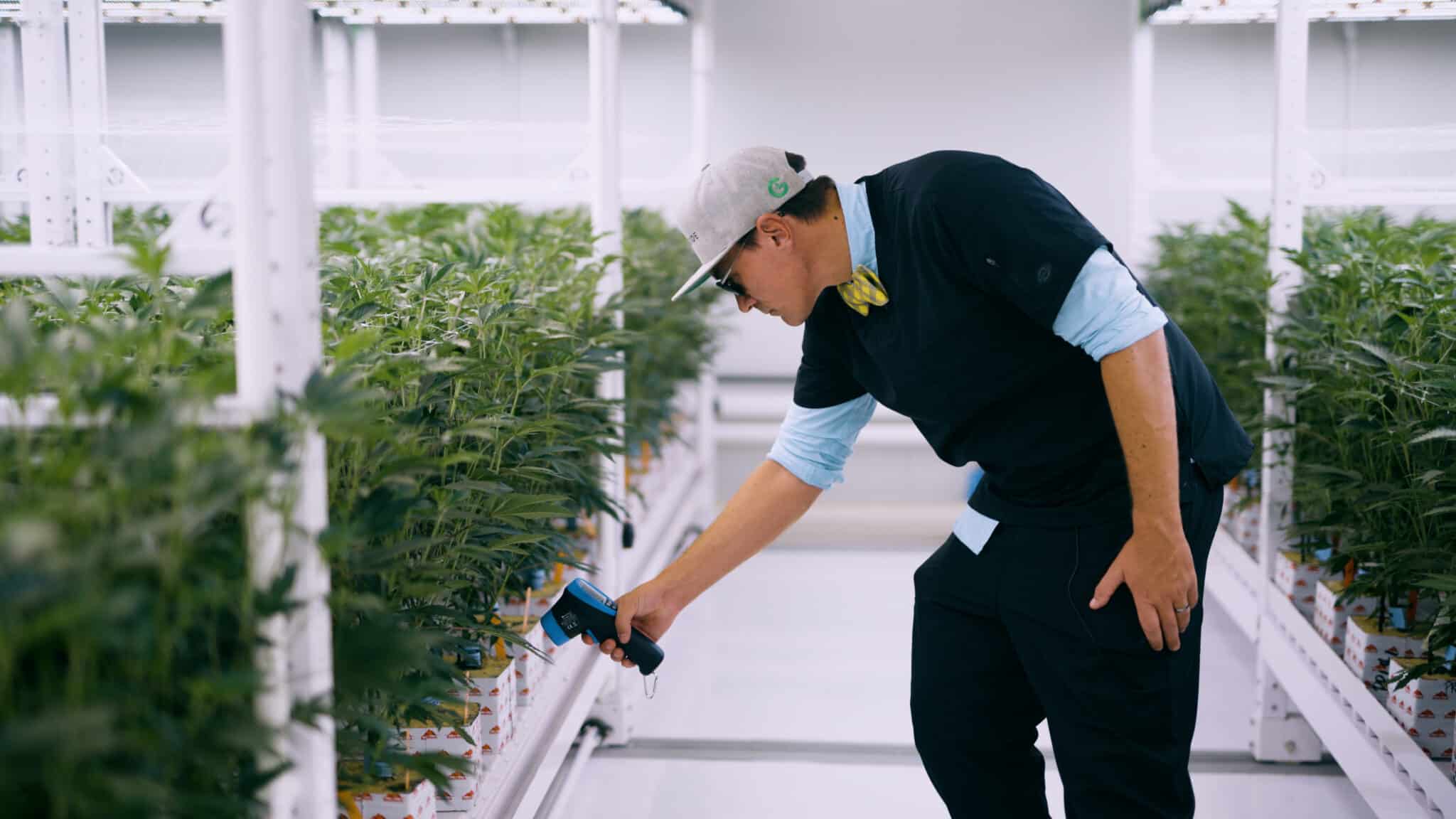
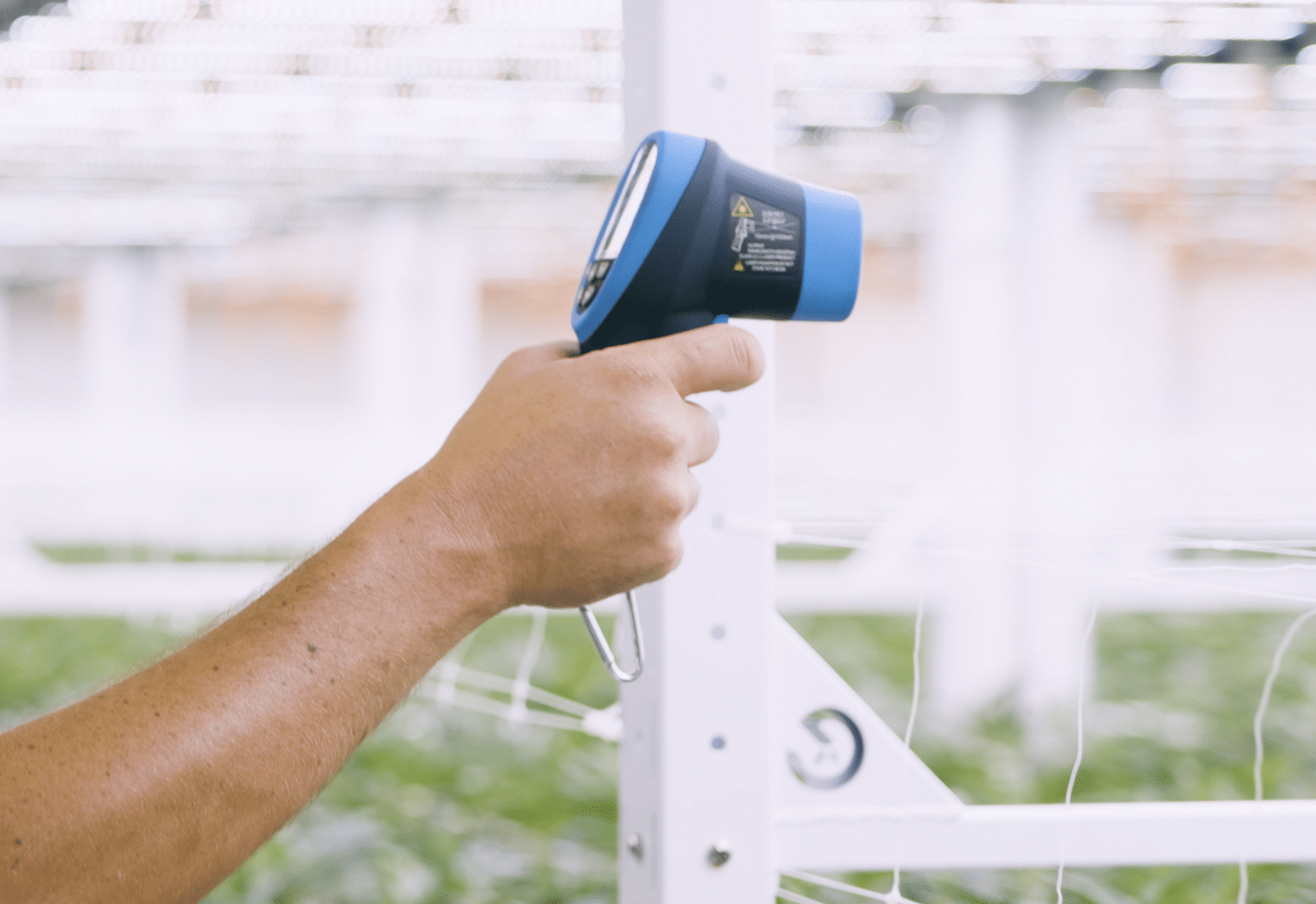
Assessing the Impact on Leaf Temperature with IR Guns:
Measuring the leaf temperature is crucial for understanding the plant’s response to the environmental conditions. Infrared guns provide a quick and non-destructive method for assessing leaf temperature. By monitoring leaf temperature, cultivators can make informed decisions on adjustments to lighting, ventilation, and HVAC systems to maintain the ideal growth conditions.
AOPUTTRIVER: IR Gun
-
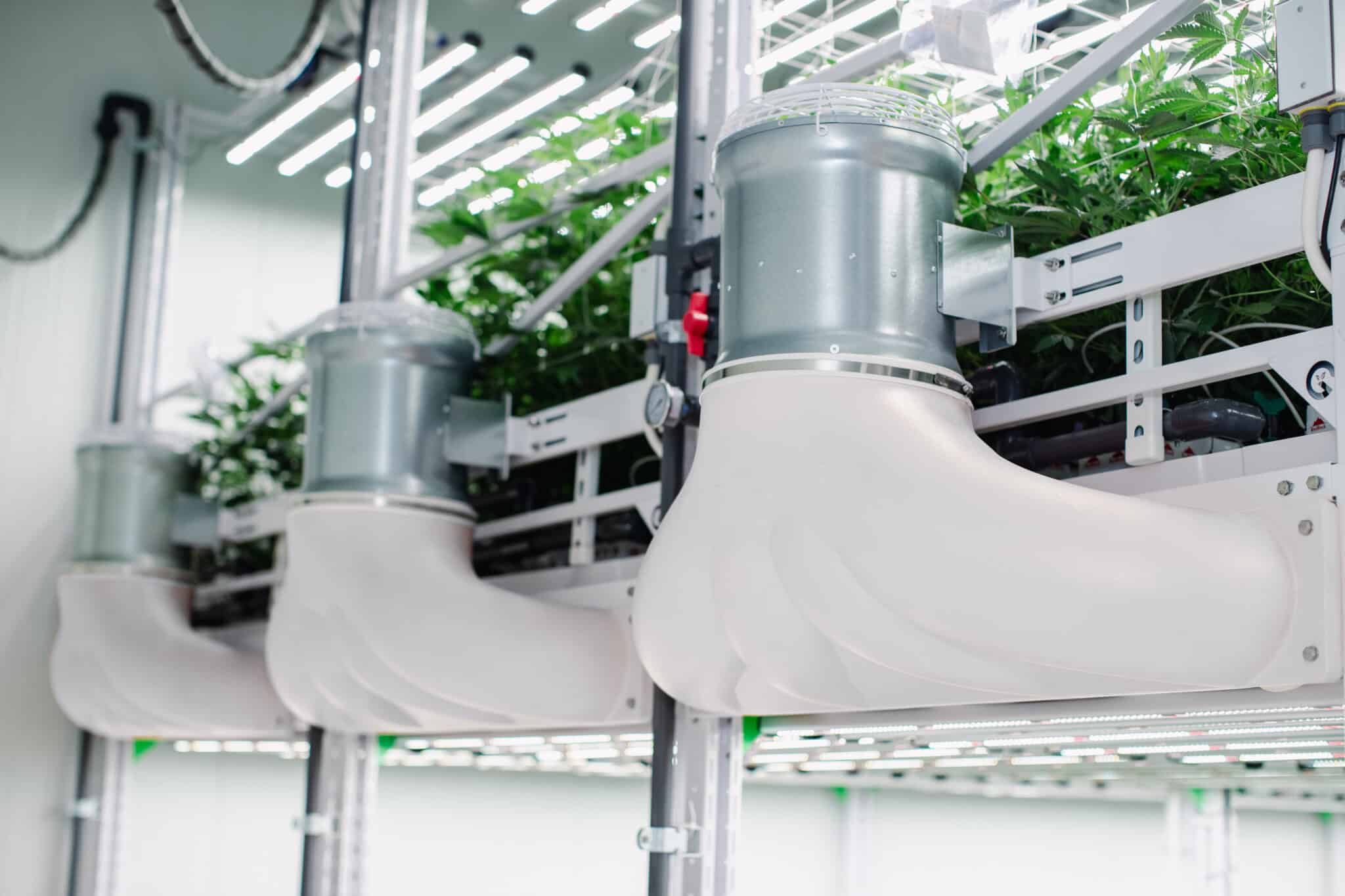
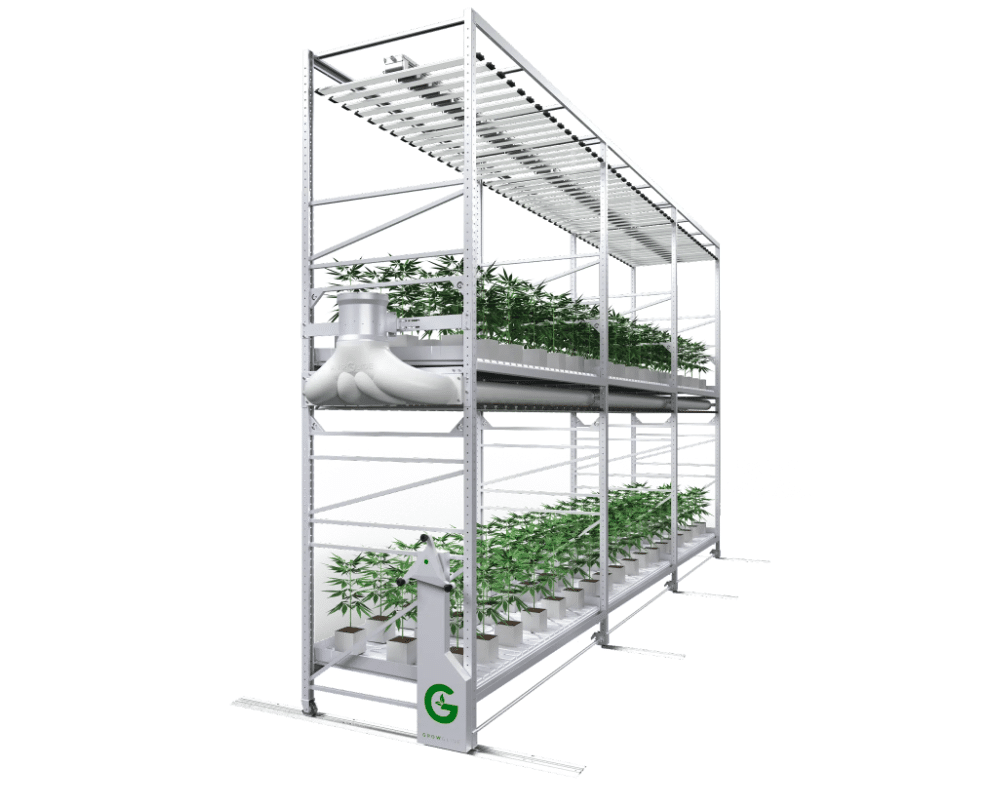
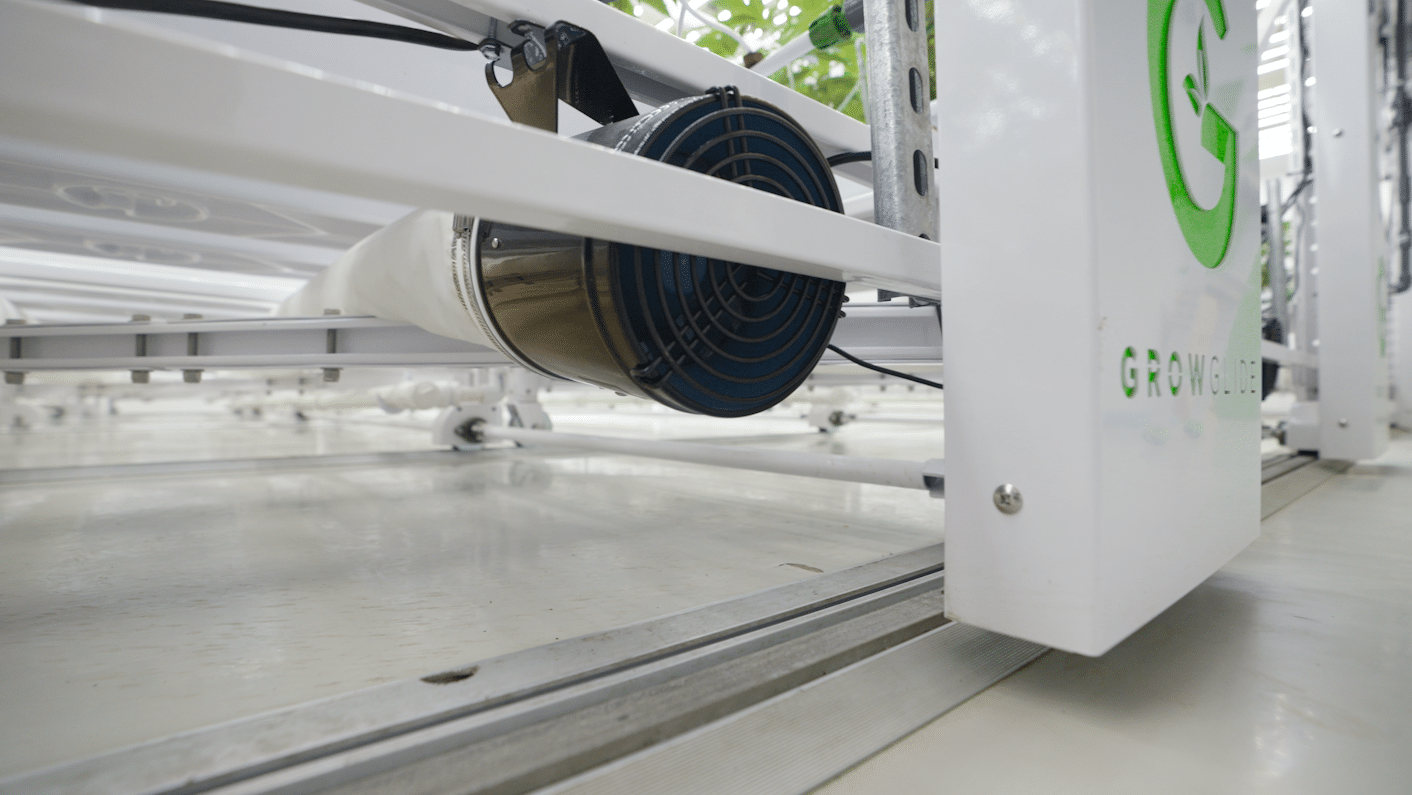
Focusing on Airflow and Efficient Use of Fans:
Proper airflow is paramount in maintaining consistent temperatures and preventing heat buildup. Fans play a pivotal role in ensuring that air circulates evenly throughout the cultivation space. The article explores techniques for optimizing fan placement and airflow patterns, leading to improved temperature control and overall plant health. Whether single-tier or multitier airflow is a paramount factor. The fans you choose and how you move air in the space directly impact plant health and operational efficiency.
Air Glide
-
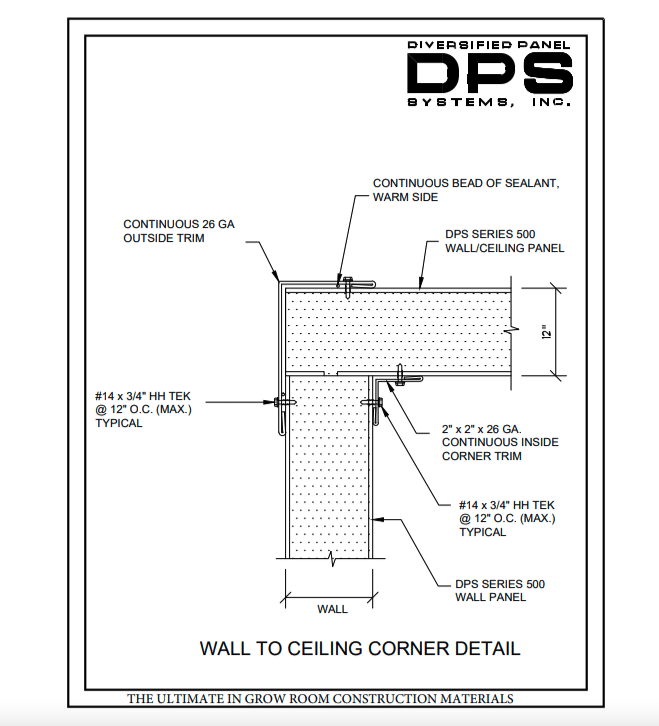
Insulated Panels:
Using insulated panels and appropriate considerations when building/retrofitting your envelope. Envelope integrity (read as leaky rooms) can significantly impact your ability to control the cultivation environment.
DPS panels
-
Root zone temperature:
Pay attention to root zone temperature. Often overlooked a root zone that is too hot or too cold will have negative impacts on yield, phenotypic expression, and bag appeal. Testing the temperature of the water delivered to the plan, the runoff temp, and the media temp will provide the granular data needed to trigger environmental setpoint and airflow changes to reduce risk and increase performance.
-
Follow the data:
Trust but verify and use the visualization of data to follow anomalies. Outliers tell you a lot about the performance of your mechanical solutions and the change needed to avoid danger zones in the future. The data can also show the impact of fertigation and IPM events, defoliation, airflow, and even heat from team members working in the space.
-
Calculating the Sensible Load in Cannabis Cultivation Spaces:
The sensible load, which refers to the heat generated by lighting, dehumidification equipment, and other factors, must be accurately determined to design an efficient HVAC system. A formula similar to Watts x 3.41 / 12,000 = tons ensures you have the capacity to manage the temperature of your cultivation space.
Conclusion:
The success of cannabis cultivation facilities heavily depends on their ability to measure and control heat. Through the use of infrared technology, remote ballasts, leaf temperature assessments, proper airflow, and accurate calculations of sensible load, cultivators can optimize their cultivation spaces for maximum yields and product quality. By implementing these strategies and staying attuned to the dynamic nature of environmental control, the cannabis industry can continue to thrive and meet the growing demand for its products.



















Leave A Comment