The concept of intracanopy lighting is not new. Historically cultivators would drop lamps without reflectors or air-cooled tubes in between ros or beastly plants to increase yield. It was usually too hot, you would burn leaves and destroy the close proximity flower to see gains a few feet away. It usually didn’t pan out.
Now with tried and true intracanopy lighting developed for CEA we can get lights closer due to less heat, prevent bleaching thanks to spectrum control, and get light to places that get dark in the late stages of growth. Intracanopy can also benefit transition plants and prevent stretch, increase production of mother plants, and accelerate the hardening-off period for veg plants.
Sounds pretty good right…so let’s dive into some of the pros and cons of intracanopy lighting for cannabis cultivation.
Schools of thought:
There are two distinct schools of thought when it comes to inter-canopy lighting applications.
- Add intracanopy and reduce top lighting to allow the plant to most efficiently utilize photonic energy. This will help reduce “B size popcorn buds” and increase the ratio of “A buds”.
- Keep top lighting high (1,000 PPFD) and add inter-canopy lighting to increase yield and optimize phenotypic expression
Grow Light Design
We have come a long way:
We have come a long way from closet grows and crappy lights to commercial facilitates with advanced technology. One of the keys to cannabis tech is that you know how to use it to reduce risk and increase financial performance. If not, it’s just a toy.
Source:
Trellising
Trellising is an effective technique for providing light to all bud sites while also providing structure to your plants and creating a more even canopy.
Source
growlightdesign
Few case studies, a few different approaches, and several reasons to consider.
- More light = increased yield. Let’s say you grow single-tier with 6-foot tall plants. How much would additional light reduce your “B-rated popcorn buds”? How much would this impact top-line revenue?
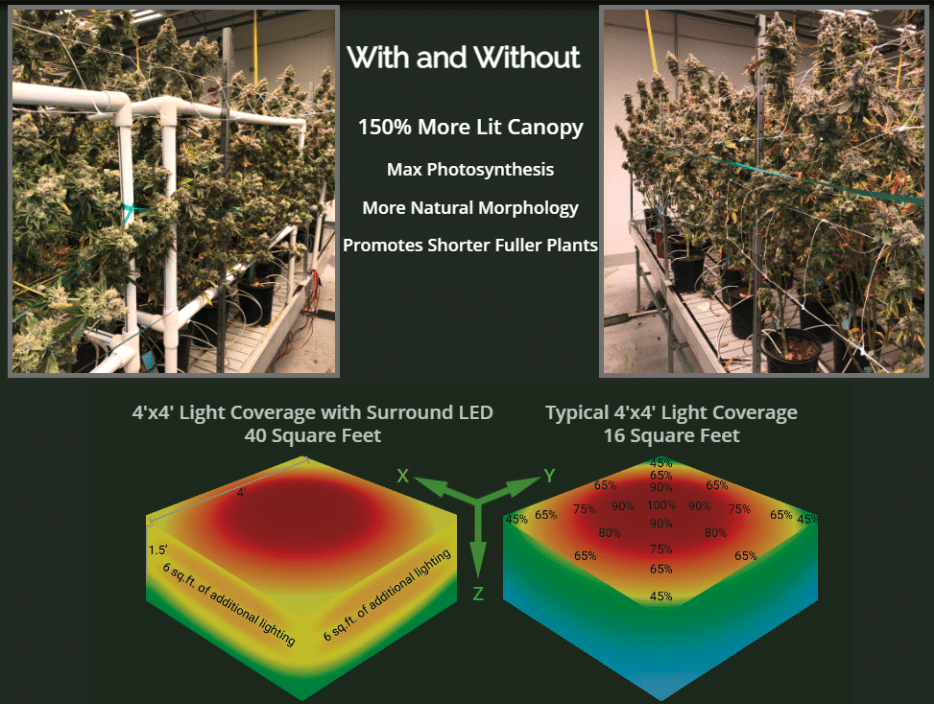
- Increased Yield: Intracanopy lighting helps to penetrate deeper into the canopy, reaching lower branches and bud sites that may not receive sufficient light from traditional top lighting alone. This can lead to increased bud development and overall yield.
- Improved Flowering and Bud Quality: By ensuring that light reaches all parts of the plant, intracanopy lighting can contribute to more uniform flowering and improved bud quality. This is especially important for cannabis cultivation where consistent quality and cannabinoid content are desired.
- Enhanced Terpene and Cannabinoid Production: Adequate light throughout the canopy can positively impact the production of terpenes and cannabinoids in cannabis plants. Terpenes are responsible for the plant’s aroma, and cannabinoids are chemical compounds with various therapeutic effects.
- Better Light Distribution: Intercanopy lighting helps to address shading issues within the canopy, ensuring that all parts of the plant receive a more even distribution of light. This can prevent lower leaves and buds from being shaded and not receiving enough light.
- Reduced Plant Stress: Providing sufficient light throughout the canopy can reduce stress on the plants. Stress can result from uneven light distribution, and addressing this through intracanopy lighting may lead to healthier, more robust plants.
- Optimized Canopy Structure: Intercanopy lighting can encourage a more open and balanced canopy structure. This can make it easier for growers to manage plants, improve air circulation, and reduce the risk of pests and diseases.
- Energy Efficiency: While intracanopy lighting involves additional lighting, it can be designed to complement top lighting systems, potentially optimizing energy use and improving overall energy efficiency.
- Customizable Light Spectrum: Intracanopy lighting systems can be customized to provide specific light spectrums that cater to the different stages of plant growth. This level of control allows growers to tailor lighting conditions to the specific needs of cannabis plants.
But what about the downside?
- Increased Energy Costs: Adding intracanopy lighting involves additional energy consumption. Growers need to assess the increased operational costs and balance them against the potential benefits in terms of yield and quality.
- Heat Generation: Intercanopy lighting can contribute to an increase in heat within the cultivation space. Managing temperatures is crucial for cannabis cultivation, and the additional heat generated by intracanopy lights may necessitate adjustments to the overall climate control system.
- Space and Infrastructure Requirements: Installing intracanopy lighting may require adjustments to the grow room or greenhouse infrastructure. This can include the installation of additional fixtures, hanging systems, and wiring. It may also affect the spatial arrangement of plants.
- Complexity in System Design: Integrating intracanopy lighting effectively requires careful planning and design. Optimizing light distribution throughout the canopy can be complex, and improper implementation may not deliver the desired results.
- Risk of Light Stress: While light is essential for plant growth, excessive light intensity can lead to light stress. It’s crucial to monitor and manage light levels carefully to avoid negative impacts on the plants, such as leaf bleaching or other signs of stress.
- Uniformity Challenges: Achieving uniform light distribution throughout the canopy can be challenging. Shading and uneven light intensity may still occur, particularly in large or densely populated cultivation spaces.
- Dependency on Strain and Growth Stage: The effectiveness of intracanopy lighting can vary based on the cannabis strain and the specific growth stage. Some strains or growth stages may benefit more from intracanopy lighting than others.
- Maintenance and Monitoring: Intercanopy lighting systems require regular maintenance to ensure consistent performance. Additionally, ongoing monitoring is essential to identify and address any issues promptly.
- Cost of Implementation: Installing intracanopy lighting systems can involve a significant upfront cost, including the purchase of additional fixtures, controls, and infrastructure modifications. Growers need to weigh these costs against the potential benefits.
- Learning Curve for Growers: Implementing intracanopy lighting effectively requires a good understanding of light distribution, plant physiology, and the specific needs of cannabis plants. Growers may need to invest time and effort in learning and fine-tuning the system.
- Variable leaf temps. VPD becomes hard to pinpoint.
Labor Concerns, Installation and Maintenance:
The initial installation of intracanopy lighting systems may require additional labor, especially if there are modifications needed to the existing infrastructure. Ongoing maintenance of these systems, including bulb replacements, checking electrical components, and ensuring proper functioning, may also contribute to labor requirements.
- Monitoring and Adjustment: Intercanopy lighting systems often require careful monitoring to ensure optimal performance. This may involve adjusting light levels, fine-tuning the spectrum, and troubleshooting any issues that arise. Growers and cultivation staff may need to spend more time on these tasks compared to traditional cultivation methods.
- Training and Skill Development: Implementing intracanopy lighting effectively requires knowledge and skills in lighting technology, plant physiology, and cultivation practices. Training staff members or hiring individuals with expertise in these areas may be necessary, impacting the labor requirements for the cultivation team.
- Harvesting and Pruning Practices: Improved light distribution within the canopy due to intracanopy lighting may influence harvesting and pruning practices. Labor requirements for these tasks could be affected as plants may have a more open canopy, making harvesting and pruning more efficient or requiring adjustments to traditional methods.
- Data Monitoring and Analysis: Some intracanopy lighting systems come with advanced controls and sensors that provide data on light intensity, spectrum, and other environmental factors. The analysis of this data may require additional labor to make informed decisions and adjustments to optimize plant growth.
- Pest and Disease Management: Changes in canopy structure and light distribution may impact pest and disease dynamics. Growers may need to adjust their pest management strategies, and increased vigilance may be necessary to monitor and address potential issues, potentially affecting labor requirements.
- Propagation and Transplanting: The improved canopy structure resulting from intracanopy lighting may influence propagation and transplanting practices. Labor requirements for these activities could be impacted, depending on how the cultivation team adapts to the changes in plant growth and spacing.
- Harvest Timing and Management: Intercanopy lighting can influence the timing of flowering and harvest. Labor requirements for managing the harvest schedule, including coordinating harvesting teams, drying, and processing, may be affected.
Source
Initial Setup Costs:
- Lighting System: Include the costs of purchasing and installing intracanopy lighting fixtures, control systems, and any necessary infrastructure modifications.
- Labor: Factor in the labor costs associated with the installation of the intracanopy lighting system.
- Electrical Upgrades: If the current electrical system needs upgrades to accommodate the new lighting, include those costs.
Operating Costs:
- Energy Consumption: Estimate the additional energy costs associated with running the intracanopy lighting system. Consider electricity rates, hours of operation, and the energy efficiency of the lighting technology.
- Maintenance: Account for ongoing maintenance costs, including bulb replacements, repairs, and any required adjustments.
Benefits:
- Increased Yield: Estimate the potential increase in yield attributed to improved light distribution within the canopy. This could be based on existing research, industry benchmarks, or your own cultivation experience.
- Crop Quality Improvement: Consider the impact of intracanopy lighting on the quality of the cannabis buds, including cannabinoid and terpene content. Higher quality products may command better prices in the market.
- Extended Growing Season: If intracanopy lighting allows for an extended growing season, factor in the additional harvests and revenue.
Operational Efficiency:
- Labor Efficiency: Assess whether intracanopy lighting improves labor efficiency in tasks such as harvesting, pruning, and monitoring. Reduced labor time may result in cost savings.
- Space Utilization: Evaluate whether intracanopy lighting allows for better space utilization, potentially increasing the overall efficiency of your cultivation operation.
Environmental Impact:
- Resource Efficiency: Consider the impact of intracanopy lighting on resource efficiency, such as water and nutrient use.
- Sustainability Benefits: If the intracanopy lighting system is designed for energy efficiency, it may contribute to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly operation.
Risk and Contingencies:
- Contingency Planning: Consider potential risks and uncertainties. Having contingency plans in place can mitigate unforeseen challenges.
ROI and Payback Period:
- Return on Investment (ROI): Calculate the expected ROI by comparing the additional revenue generated (benefits) to the total costs.
- Payback Period: Determine how long it will take for the benefits to offset the initial investment and when you can expect a positive return.
Conclusion:
the exploration of intracanopy lighting solutions in cannabis cultivation unveils a dynamic landscape of possibilities and challenges. The resurfacing of this cultivation strategy, bolstered by advancements in LED technology, beckons growers to reconsider the once-dismissed idea of strategically placing lights within the canopy. The potential benefits, ranging from increased yield and improved quality to optimized canopy structures, offer a tantalizing prospect for cultivators seeking to elevate their operations.
However, the journey toward harnessing the full potential of intracanopy lighting is not without hurdles. From the increased energy costs and heat generation to the intricacies of system design and the ever-present risk of light stress, growers must navigate a complex terrain. The dependency on strains and growth stages, coupled with the learning curve for effective implementation, adds layers of consideration for those contemplating the integration of intracanopy lighting.
As with any innovation in cultivation practices, the key lies in a thorough and balanced assessment. Growers must meticulously weigh the potential benefits against the incurred costs, both upfront and operational. The decision to adopt intracanopy lighting should be informed by a deep understanding of the specific needs of the cannabis plants, coupled with a commitment to ongoing monitoring, maintenance, and potential adjustments.
In essence, intracanopy lighting stands as a testament to the evolving nature of cannabis cultivation practices, where technological advancements empower growers to revisit and refine age-old strategies. The future holds promise for those who dare to venture into this realm, armed with a nuanced understanding of the pros and cons, and a commitment to cultivating not just plants, but a sustainable and efficient future for cannabis production.
Additional resources
2. Intercanopy Lighting Produces 20% Yield Surge and 27% Larger Buds



















Leave A Comment