When I first heard about being exposed to gamma gadiation, I thought, well, it worked for Bruce Banner. But then reality set in, and I was reminded that I did not want to be a massive green humanoid with incredible strength and uncontrollable anger. Don’t get me wrong, I love to consume the Bruce Banner cultivar, but I don’t want to consume gamma radiation. Who knows, maybe I have already done so and didn’t even know it.
As two studies highlight, cannabis remediation is a hot-button topic, especially when large-scale crop failures occur. Destroying acres of cannabis can cost millions, and this has given rise to the remediation industry. [1,2]
What is remediation? Cannabis remediation refers to the process of reducing or eliminating contaminants from cannabis plants or cannabis-derived products. Contaminants can include various substances such as pesticides, heavy metals, residual solvents, microbial organisms, and mycotoxins.
Why Do You Need Remediation?
Because you failed your COA test for microbial contamination — or you were about to.
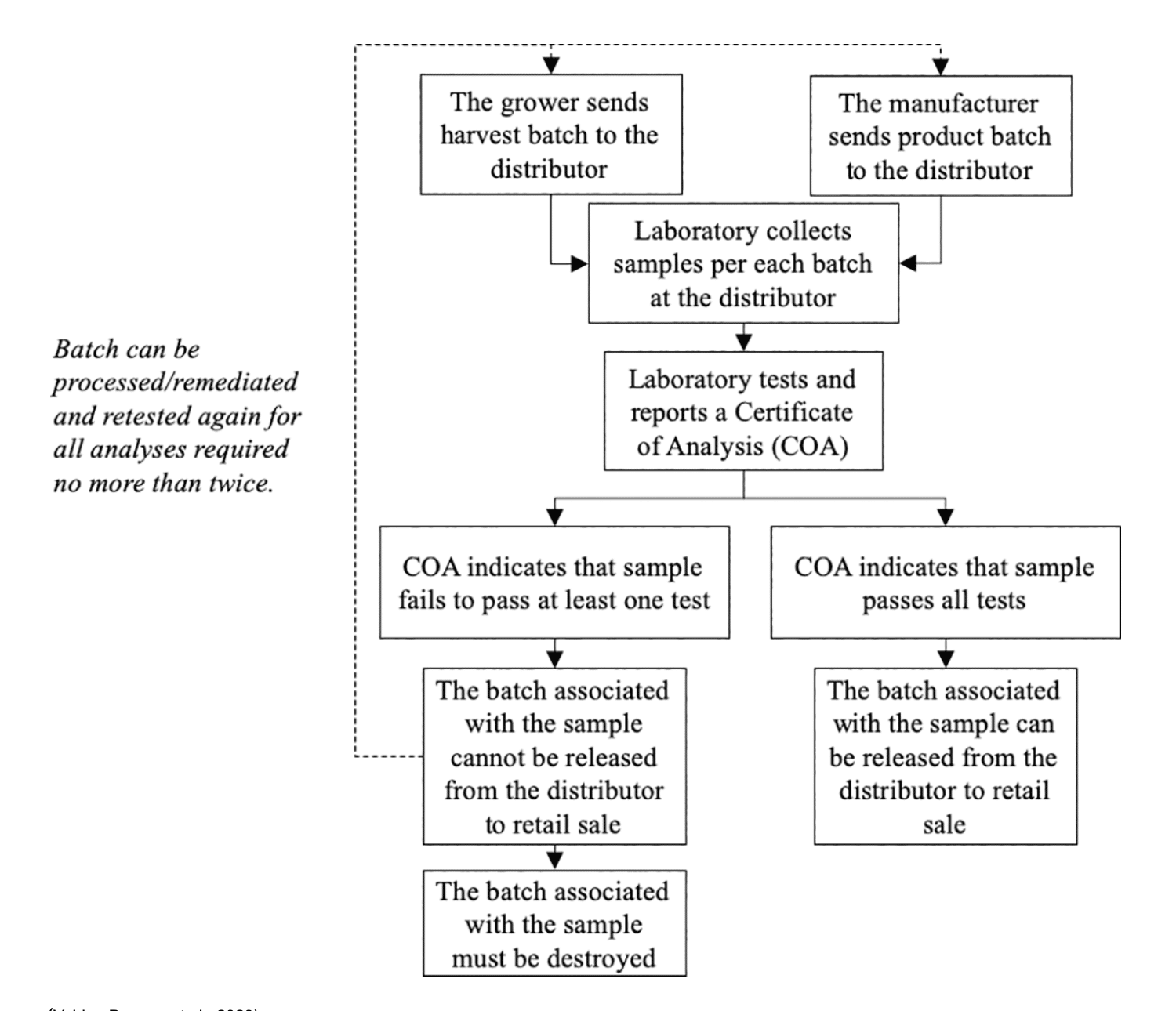
Here is a visual of the process:
(Valdes-Donoso et al., 2023)
You messed up. Your facility was poorly designed, from filtration to standard operating procedures (SOPs) to mechanical solutions. Your integrated pest or microbe management (IPM/IMM) was ineffective. Your curing process was uninformed. You grew as much mold, mildew, and yeast as you did THC. And now you have a bunch of pounds of poison weed. Now what?
No one wants to remediate, but it becomes a necessary evil when the core goal is to ensure your business’s survival, especially when you’re tasked with making payroll. The options at your disposal, each with its pros and cons, can seem daunting. You can opt for extraction to separate your cannabis from its contaminants. Alternatively, there is gamma radiation and ozone treatment, which, while sounding as superheroic as a Bruce Banner transformation, are valuable methods for removing impurities.
However, these processes have significant financial implications, and there may be instances where disposal, regardless of its high cost, becomes the only option. In these cases, repercussions can be harsh. You may end up firing a team member or worse, see your whole business crumble.
Thankfully, the cannabis industry has adopted Certificates of Analysis (COAs) to streamline safety (and pricing) in this emerging market, helping businesses alleviate the burdens associated with remediation.
Why Are COAs Crucial for Cannabis?
Certificates of Analysis (COAs) are crucial documents that provide detailed information about the quality, potency, and safety of cannabis products. They are typically generated by third-party laboratories that conduct comprehensive testing on cannabis samples. Here are the key reasons why COAs are important for cannabis:
- Quality Assurance: COAs provide a snapshot of the product’s quality and consistency. They contain information about the cannabinoid profile, including the levels of THC, CBD, and other cannabinoids present in the product. This helps consumers and businesses assess the potency and composition of the product, ensuring that it meets their specific requirements.
- Safety and Compliance: COAs play a vital role in ensuring the safety of cannabis products. They provide information on the absence or presence of various contaminants such as pesticides, residual solvents, heavy metals, microbial organisms, and mycotoxins. By having access to this information, consumers can make informed decisions about the safety and suitability of the product for their needs.
- Regulatory Compliance: In many jurisdictions, cannabis products are subject to strict regulatory requirements. COAs help demonstrate compliance with these regulations by providing evidence of testing and adherence to safety standards. Regulatory authorities may require specific limits or thresholds for contaminants, and COAs allow businesses to verify that their products meet those requirements.
- Consumer Confidence: COAs contribute to building trust and confidence among consumers. By providing transparent and verifiable information about the quality and safety of cannabis products, COAs empower consumers to make informed choices. They can verify the authenticity of product claims, ensuring that they receive the desired potency and purity.
- Supply Chain Integrity: COAs are essential for maintaining transparency and accountability throughout the cannabis supply chain. From cultivation and processing to distribution and retail, COAs serve as a record of product quality and safety. They help identify potential issues or discrepancies and facilitate traceability, ensuring that the product can be traced back to its origin.
The Price of a Failed Microbial Test
The remediation process is typically carried out to ensure that cannabis products meet regulatory standards and are safe for consumption. Contaminated cannabis products may pose health risks to consumers, so it is essential to remediate them to minimize potential harm.
The cost of a failed microbial test for a batch of cannabis can vary depending on several factors, including the regulations of the specific jurisdiction, the size of the batch, and the intended use of the cannabis product. Here are some potential costs associated with a failed microbial test:
- Loss of the Batch: In many cases, a failed microbial test may result in the entire batch being rejected and deemed unfit for sale. This can lead to a significant financial loss for the producer or manufacturer, as they may need to dispose of the batch and incur expenses for its destruction.
- Re-Testing and Re-Labelling: After a failed microbial test, the producer may re-test the batch to confirm the results. This involves additional costs for sampling, testing, and potentially using a different testing laboratory. If the re-test shows the same microbial contamination, the batch may need to be discarded, further increasing costs.
- Remediation Expenses: If the producer intends to salvage the batch, they may opt for microbial remediation techniques to reduce or eliminate the contaminants. The costs associated with remediation methods, such as heat treatment, sterilization, or biological remediation, can vary depending on the techniques employed.
- Delayed Time to Market: A failed microbial test can delay bringing the product to market. This delay can impact sales and revenue projections, potentially resulting in financial losses for the producer or manufacturer.
- Reputational Damage: Failed microbial tests can harm the reputation of the producer or manufacturer. Adverse publicity or consumer mistrust can lead to decreased demand for their products and potential long-term financial cons.
Remediation Techniques: The Final Rescue for Contaminated Cannabis
Different methods are employed for cannabis remediation, depending on the specific contaminants present. Here are some common techniques:
- Extraction and Filtration: Solvents like ethanol or CO2 are used to extract cannabinoids and terpenes from the plant material. Filtration processes can then remove particulates and some contaminants, but your concentrates might also fail COA testing.
- Chromatography: This method involves using chromatographic techniques, such as high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), to separate and remove specific compounds, such as pesticides or mycotoxins, but this is expensive and complicated.
- Heating and Drying: Certain contaminants, such as residual solvents, can be removed by subjecting the cannabis material to controlled heating and drying processes but this will ruin the final product.
- Biological Remediation: Microorganisms can be used to break down or metabolize contaminants in a process called bioremediation. For example, specific strains of bacteria or fungi can be employed to degrade pesticides or hydrocarbons, but you won’t be able to sell the final product.
- Water-Based Remediation: Some contaminants, such as heavy metals, can be removed using water-based methods like filtration, precipitation, or ion exchange, but you will still have microbes to worry about.
- Gamma Radiation: This process involves exposing cannabis products to gamma rays emitted by a radioactive source in a controlled and regulated environment, but you might turn into the Hulk if you consume the final product.
- Ozone: Ozone remediation for cannabis refers to the use of ozone gas to eliminate or reduce contaminants, such as microbial organisms, on cannabis plants or cannabis-derived products. Some, like Willow Industries make a good case for this technology being the best option!
The Gamma Radiation Process: A Closer Look
Gamma radiation is a type of electromagnetic radiation that consists of high-energy photons. It is produced through the decay of radioactive isotopes, such as cobalt-60 or cesium-137. Gamma radiation is commonly used in various industries for sterilization purposes, including the medical field, food industry, and, in some cases, the cannabis industry.
In the context of cannabis, gamma radiation can be used as a method of microbial remediation or sterilization to eliminate or reduce microbial contaminants, such as bacteria, yeast, molds, and fungi.
Here is an overview of how gamma radiation is used on cannabis:
- Irradiation Facility: A specialized facility equipped with gamma irradiation equipment is used to carry out the process. The facility must comply with relevant safety regulations and have proper shielding to protect workers and the environment from radiation exposure.
- Product Preparation: The cannabis products, typically dried flowers or extracted material, are carefully packaged and prepared for irradiation. Proper packaging materials that allow penetration by gamma rays, such as low-density polyethylene (LDPE), are used.
- Irradiation Process: The packaged cannabis products are placed in a controlled chamber. The gamma radiation source, often cobalt-60 or cesium-137, emits high-energy photons that penetrate the packaging and interact with the microorganisms present in the product. These interactions disrupt the microbes’ DNA and other cellular components, rendering them inactive or unable to reproduce.
- Dosage Control: The duration and intensity of the gamma radiation exposure are carefully controlled to ensure effective microbial remediation while minimizing potential damage to the cannabinoids and other components of the cannabis product. Dosage is typically measured in kiloGrays (kGy) unites, with the specific dosage requirements varying depending on regulatory standards and product specifications.
- Quality Control and Testing: After the irradiation process, the cannabis products are typically subjected to further testing, including microbial analysis and other quality control procedures, to ensure that the desired standards for safety and quality are met.
It’s important to note that while gamma radiation can effectively reduce microbial contaminants, there are ongoing discussions and debates about potential effects on the flavor, aroma, and overall quality of cannabis products. Some argue that irradiation may cause the degradation of certain compounds, such as terpenes, potentially impacting the product’s sensory characteristics.
Regulatory frameworks differ across jurisdictions regarding the use of gamma radiation on cannabis. Cannabis producers need to comply with applicable regulations and adhere to established guidelines to ensure the safety and quality of their irradiated products.
The Ozone Remediation Process: A Closer Look
Ozone (O3) is a highly reactive molecule composed of three oxygen atoms. This reactivity means ozone can be a powerful weapon against various contaminants. It works by destroying or altering the structures of both organic and inorganic contaminants, such as bacteria, molds, fungi, and even certain chemicals.
The process of ozone remediation typically involves the following steps:
- Ozone Generation: Ozone gas is generated using specialized ozone generators. These generators convert molecular oxygen (O2) into ozone (O3) through various methods, such as corona discharge or ultraviolet radiation.
- Ozone Application: The ozone gas is introduced into an enclosed environment, such as a sealed chamber or a controlled processing area. Cannabis plants or cannabis products are exposed to the ozone gas within this environment.
- Ozone Oxidation: Ozone is a powerful oxidizing agent. It reacts with organic and inorganic compounds, including microbial organisms, by breaking down their cell walls and interfering with their metabolic processes. This oxidative effect helps eliminate or reduce contaminants, including bacteria, molds, fungi, and other microorganisms.
- Contact Time and Concentration: The duration of ozone exposure and the concentration of ozone gas are critical factors in the remediation process. These parameters are carefully controlled to ensure effective microbial reduction while minimizing potential damage to the cannabis product.
- Air Filtration and Safety Measures: Ozone can be harm humans and damage lung tissues when inhaled in high concentrations. Therefore, proper air filtration systems and safety measures, such as appropriate ventilation and protective equipment for workers, are essential during the ozone remediation process to prevent ozone exposure.
- Residual Ozone Removal: After the ozone remediation process, residual ozone needs to be removed from the cannabis product. This is typically achieved by allowing the product to undergo a period of “off-gassing” in a well-ventilated area, ensuring that ozone levels are reduced to safe and acceptable levels.
Ozone remediation should be conducted by experienced professionals knowledgeable about the process and safety guidelines. Ozone remediation can be an effective method for reducing microbial contaminants in cannabis, but it should be implemented in compliance with relevant regulations and standards to ensure the safety and quality of the final product.
It’s important to note that the specific remediation method used may vary depending on the legal and regulatory requirements of the jurisdiction where the cannabis products are being produced or sold. Different regions may have specific limits for permissible levels of contaminants, and the remediation process aims to bring the products within those limits for compliance and safety.
Cost Implications of Cannabis Remediation
Cannabis product remediation can have an impact on the price of the final product. The specific effects on pricing will depend on various factors, including the extent of the remediation required, the cost of the remediation process itself, and market dynamics. Here are some ways in which remediation can affect the price of cannabis products:
- Cost of Remediation: The expenses associated with the remediation process, such as testing, equipment, personnel, and any necessary treatments or technologies, can add to the production costs. These costs are likely to be passed on to the consumers, potentially increasing the product’s price.
- Batch Rejection: In some cases, if a cannabis batch fails remediation or cannot be remediated effectively, it may need to be discarded or destroyed. This can result in significant financial losses for the producer, which may also affect the overall pricing strategy for their products.
- Additional Testing: Remediation may require further testing before and after the process to ensure the efficacy and safety of the product. This additional testing can contribute to the overall costs and, consequently, the price of the cannabis product.
- Market Demand and Perception: The market demand for safe and high-quality cannabis products can influence pricing. If consumers prioritize safety and are willing to pay more for products that have undergone rigorous remediation, producers may price their remediated products at a premium. On the other hand, if consumers are more price-sensitive and do not prioritize remediation, the price impact may be minimal.
- Regulatory Compliance: Compliance with regulatory requirements is essential for cannabis producers. If extensive remediation is necessary to meet regulatory standards, the associated costs can impact the product’s price. Stricter regulations and testing requirements may increase production costs, which can be reflected in higher product prices.
Is Remediated Cannabis Safe?
Remediated cannabis, when done properly and in compliance with regulatory standards, can be safe to consume. The purpose of cannabis remediation is to reduce or eliminate contaminants that may pose health risks to consumers. Remediation methods are employed to bring cannabis products within acceptable safety limits for various contaminants, including pesticides, heavy metals, microbial organisms, residual solvents, and mycotoxins.
However, it’s important to note that the safety of remediated cannabis products depends on several factors:
- Method Validation: The chosen remediation method should be scientifically validated and proven to effectively reduce or eliminate contaminants without adversely affecting the quality or safety of the product. Validated methods ensure that the remediation process is reliable and consistent.
- Regulatory Compliance: Compliance with applicable regulations and safety standards is crucial. Cannabis producers must follow the guidelines and limits set by regulatory authorities to ensure that the remediated product meets safety requirements.
- Quality Assurance: Comprehensive testing, including before and after remediation, is essential to verify the effectiveness of the process and ensure that the product is safe for consumption. Independent third-party testing laboratories can provide objective assessments of the product’s safety and quality.
- Proper Dosage and Concentration: If the remediation process involves using chemicals or other agents, it’s essential to ensure that any residues left behind are within safe and acceptable limits. Strict adherence to dosage and concentration guidelines is crucial to avoid potential adverse effects on consumer health.
- Product Handling and Storage: Proper handling, storage, and packaging of the remediated cannabis products are crucial to maintain their safety and prevent recontamination. Good manufacturing practices (GMP) and proper storage conditions are essential to ensure product integrity.
Taking Ownership: The Key to a Successful Cultivation Facility
The bigger lesson is that designing a commercial cultivation facility is different than running a tent grow, a closet operation, or even an illegal 100-light warehouse. You need to understand how to use the tools you have invested in. Did you understand how your HVACD system was sized, or did you assume someone else would do it for you? Did you understand airflow, air exchanges, and air filtration, or did you assume someone else would get it right? Did you think through your drainage and cleaning plans, or did you trust the plumber down the street to guide your success? Did you write nimble SOPs adapted to granular inputs, or did you assume your consultant would nail it for you? A facility built on these assumptions will be a lousy facility. Don’t assume, don’t scapegoat, don’t blame the ignorance of others. Take ownership of the decision-making process, empower yourself with knowledge, surround yourself with purpose-built solutions and experience — and understand the why of every dollar you spend.
Avoid the costs of remediation (and ridicule) by building a manageable facility. Bring in experts that solve problems, reduce risks, and empower YOU to be successful. No one is going to grow weed for you. You need to own every part of the process. So own your racking decisions, your airflow decisions, your HVACD and control decisions, and know why you spent the money to get the solutions you need to succeed.
In short, don’t build a bad facility, or you will have to remediate your product. And if you do have to remediate your product, know what you are using, why you are using it, and learn how to prevent it in the future.
If remediation must be done, adhering to these factors, cannabis producers can mitigate risks and ensure that their remediated cannabis products are safe for consumption. Consumers should also ensure they purchase cannabis products from reputable sources that provide detailed information about the remediation process, third-party testing, and compliance with safety regulations.
And let’s require any remediated cannabis to be labeled as such so we don’t go around creating accidental superheroes . . . or supervillains.
[1] Valdes-Donoso, P., Sumner, D. A., & Goldstein, R. S. (2020). Costs of cannabis testing compliance: Assessing mandatory testing in the California cannabis market. PLOS ONE, 15(4), e0232041. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0232041














Leave A Comment